
Solar Calculator
Instantly estimate the solar capacity you need, how much it’ll cost, and your solar power buyback period.
What is a solar calculator?
A solar calculator helps you design solar power systems, estimate prices, and predict energy savings.
It can quickly calculate different solar energy concerns, such as:
Panel sizing and system pricing
Power consumption estimates
Energy output and capacity
Installation costs
Electric bill savings
Return on investment
Payback periods or break-even points
Solar financing
And more
Our solar calculator lets you easily see which solar option is best for you. The results give you an idea of the costs and potential savings.
How to calculate solar power payback period
Customers often use solar calculators to help them understand how a solar power system can lower their electric bills. The calculated savings let you estimate how many years it'll take to see a return on investment (ROI).
In the solar energy industry, this is known as the payback period. ROI is likely a huge consideration when you're deciding on solar energy.
Here's a simple way to calculate the payback period for solar power. Take the total system cost and divide it by the estimated annual savings on electricity costs.
To calculate annual savings, subtract the new average electric bill from the average of the old bill and multiply it by 12 months.
Example:
Say a solar power setup costs $10,000 all up. This new solar array can cut your electric bill in half from $200 to $100 a month, which adds up to $1,200 in yearly savings.
To get the estimated payback period, divide the $10,000 with the estimated annual energy savings of $1,200
This sample solar power system will have paid for itself in about 8 years and 4 months. And it'll continue to save you money for many years to come.
How to calculate solar power system size
The size of your solar power system should suit your specific requirements. Solar power calculators are invaluable tools for determining how big the solar panel array should be.
This lets you know if it can reliably power essential electrical appliances, especially if the system is off-grid.
There are many factors to consider when choosing a solar power system. The more prominent ones include:
Energy and kWh requirements
Solar array size
Number of solar panels required
Solar panel efficiency
Battery capacity
Sun exposure (solar hours per day)
Roof area (square footage) and angle
It’s hard to consider all these specifications and data all in one go, especially for someone new to solar energy. But a solar calculator can make short work of the task and give out estimates and recommendations quickly.
To calculate your energy requirements, check how many watts an electrical appliance consumes. Multiply the wattage by the number of hours it’s used per day. This gives you the number of watt hours it needs daily.
Add up the watt hour usage for your most important appliances and devices to figure out how many watt-hours you’ll need from your solar power system daily.
Example:
Let’s get the total energy usage for these appliances.
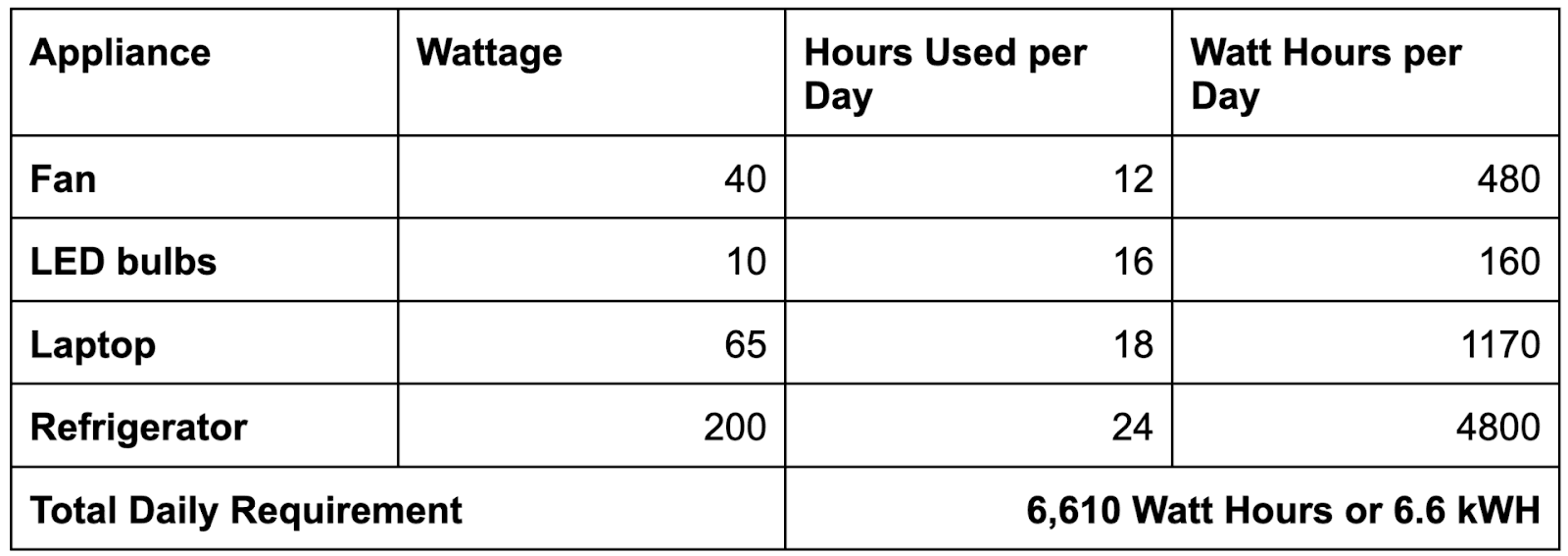
For completely off-grid operation, we’ll need a solar power system that delivers at least 6.6 kWh daily.
Want to reduce your electric bill by half? You’ll need a system that can produce roughly 3.3 kWh per day.
For any solar power system, you’ll need to account for variances like cloudy days and other less-than-ideal situations. So it’s better to oversize to compensate for any unforeseen circumstances.
How to calculate solar output
A solar panel’s output is rated in watts. Output can range from a couple of watts for portable use to over 400 watts for high output models.
How do you calculate a solar panel array’s total output? You first must check each panel’s wattage rating before multiplying it by how many hours of sunlight it gets every day.
To get the entire panel array’s total output, simply add up the daily output of all the solar panels in the system.
Example:
Say your solar panel array has six 250-watt solar panels and gets an average of 5 hours of sun daily. It can produce up to 7,500 watt hours of energy.
How do I calculate solar energy capacity?
Have you ever thought about how many hours or days a solar-powered electrical system will last in case of a power outage? The answer depends on the total output of the solar panel array and the size of the battery bank.
Solar panels can provide power to a device without being hooked up to a battery. But a battery bank can store any extra electricity the panels produce and provide electricity when the sun sets.
Powering high-wattage appliances is also easier with a battery bank when a solar array’s total output is not enough.
Batteries used in solar power systems are typically 12-volt, 24-volt or 48-volt varieties and are rated in amp-hours. These get hooked up to an inverter to convert electricity from DC to AC to power household appliances.
Since batteries are rated in amp-hours, a 120 amp-hour battery can constantly deliver 5 amps for 24 hours. Alternatively, it can also supply 20 amps for 6 hours.
Say you need to power an appliance on a 12-volt solar battery for 10 hours. The appliance draws 165 watts from the wall. You'll need 1,650 watt-hours or 1.65 kWh of electricity.
Remember that Watts = Volts x Amps. Taking the total power consumption and dividing it by the voltage of the battery system will give you the necessary battery amp-hour rating.
But solar power batteries aren’t supposed to lose more than 50% of their rated capacity. So, you’ll need to multiply the amp-hour rating by at least 2 to avoid premature battery wear.
Your battery bank must have at least 275 amp hours to power the 165-watt appliance for 10 hours straight. You’ll need 660 amp hours of capacity for it to reliably last for 24 hours.
How many solar panels will I need?
Check your average monthly electric consumption and divide it by 30 to get your daily average.
Let’s say your monthly bill shows that you average around 450 kWh monthly.
Now, let’s try to figure out how many 250-watt solar panels you’ll need to completely run on solar power.
Calculate each panel’s daily energy production by multiplying the watt rating by the number of hours it gets direct sunlight, also known as peak sun hours. Most places get at least 4 hours per day so let’s try that.
To cover your daily power consumption, you’ll need at least 15 250-watt solar panels.
Share this calculator