
Calorie Calculator
Quickly and easily determine your optimal daily calorie intake based on age, gender, weight, height, and activity level.
What is a calorie calculator?
A calorie calculator helps you quickly figure out your ideal daily calorie needs based on information like age, gender, weight, height, and activity level.
The data is then run through an equation. This calculates the calories you must consume daily to maintain the same body weight.
A calorie calculator can also tell you how many calories you need to remove if you want to create a deficit and lose weight or add if you’re trying to gain weight.
Benefits of a calorie calculator
A calorie calculator is essential for tracking your daily eating habits and nutritional needs. The tool helps you achieve your personal weight targets and health goals.
Businesses can also use calorie calculators to attract and educate their audiences. You’ll see calorie calculators used in the following industries:
Healthcare
Nutrition
Fitness
Sports
Personalized calorie intake
A calorie calculator helps determine the daily caloric needs based on age, gender, weight, height, activity level, and goals (e.g., weight loss, maintenance, or gain). This personalized approach provides a more accurate estimate than generic guidelines.
Supports weight management goals
Knowing your daily calorie requirements helps you create an effective weight loss, gain, or maintenance plan. You can adjust your intake to create a calorie deficit (for weight loss) or surplus (for weight gain) in a controlled way.
Promotes nutritional awareness
Using a calorie calculator encourages mindfulness about what and how much you eat. It helps you understand the energy content of different foods. This makes it easier to make healthier choices and avoid overeating.
Helps track progress
Monitoring daily calorie intake and comparing it to your target means you can track your progress over time. This simplifies identifying patterns, adjusting habits, and staying motivated.
Setting realistic goals
A calorie calculator offers a clear blueprint for how many calories you should consume, helping you set realistic and achievable goals. You can prevent frustration by setting unrealistic expectations.
Aids balanced nutrition
Many calorie calculators suggest macronutrients (protein, carbohydrates, fat) based on your goals. This makes your diet not just about calories but also about achieving balanced nutrition for overall health.
Supports exercise and activity planning
Accounting for your activity level lets you know how much exercise influences your daily caloric needs. This makes it easier to integrate exercise into your routine and understand its impact on your overall energy balance.
Managing medical conditions
Calorie calculators are valuable for managing dietary needs and controlling intake. They can help people manage conditions like:
Obesity
Diabetes
Hypertension
Encourages accountability
Having a clear calorie intake target encourages accountability. Regularly tracking your intake helps you stay on course, make informed choices, and understand the impact of your eating habits on your goals.
How many calories do I need in a day?
Your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) and Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) determine your daily calorie requirement.
BMR is the energy your body consumes when you're at complete rest, not doing anything at all. You might consider it the minimum calories your body needs to stay alive.
There are many formulas to estimate your BMR, but the most widely used one today is the Mifflin St. Jeor equation.
BMR calculations differ for men and women because of the many variations in body composition, such as muscle mass and fat.
BMR for men:
BMR for women:
To convert centimeters into feet and kilograms into pounds, use the following formulas:
With a calorie calculator, you can make life easier for yourself. Choose between imperial and metric units so you can get results in seconds.
Once you’ve figured out your body’s BMR, you can estimate your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE). This accounts for the extra calories you need to sustain your daily physical activities.
Even if you have a very sedentary lifestyle and don’t go out at all, you’ll still need to add calories on top of what your BMR requires to not lose muscle mass and fat - unless you’re suffering from a medical condition that requires you to be bedridden all day.
To estimate your TDEE, you must apply these multipliers to your BMR:
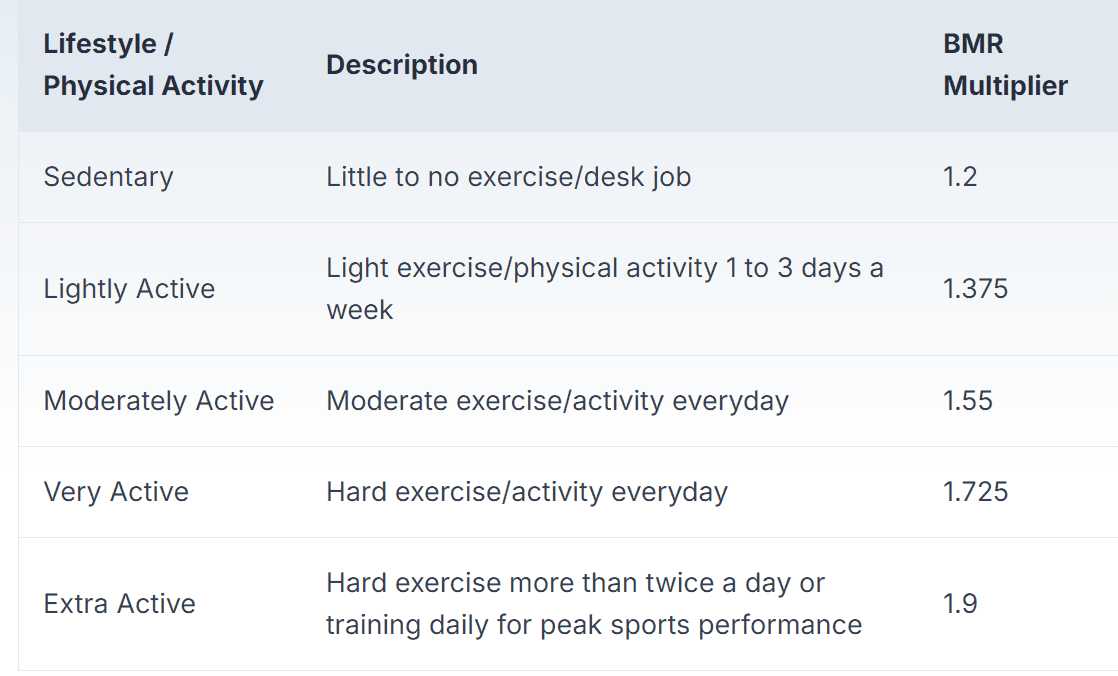
BMR and TDEE example 1
Let’s calculate the TDEE for a 30-year-old male construction worker who weighs 180 pounds and is 6 feet tall.
First, we need to convert the imperial measurements to the metric system.
180 pounds ÷ 2.205 = 81.63 kilograms 6 feet x 30.48 = 182.88 centimeters
Now, let’s figure out this individual’s BMR:
Our subject does a lot of heavy lifting, climbing up and down ladders, walking, and other manual labor tasks. We can classify his level of physical activity as ‘Very Active’ and assign him a multiplier of 1.725.
To maintain the same body weight, he should consume around 3,130 Calories daily.
BMR and TDEE example 2
Now, let’s check out the TDEE for a 30-year-old female executive. She spends most of her time in the office but goes to the gym a few times a week.
The woman is 5’5” tall and weighs 130 pounds.
130 pounds ÷ 2.205 = 58.96 kilograms
Let’s also convert her height from feet and inches to centimeters:
5 foot 5 inches = 65 inches = 5.42 feet 5.42 feet x 30.48 = 165 centimeters
Now, we can estimate her BMR:
Our subject spends most of her workday sitting in front of her computer and attending meetings. But she makes a point of going to the gym, jogging or doing yoga 2 to 3 times a week.
We can classify her level of physical activity as ‘Lightly Active’ and assign a TDEE multiplier of 1.375.
To maintain the same body weight, she should consume around 1,802 Calories daily.
Share this calculator